J4 grade stainless steel is manganese and chromium-based austenitic stainless steel having a moderate amount of nickel, copper, and nitrogen.
J4 stainless steel is widely used in commercial and industrial applications because of its high corrosion resistance, which is the result of its specific chemical composition.
This can heavily contribute towards the results that you will be able to get at the end of the day.
Let’s keep reading.
What is J4 Stainless Steel?
J4 grade is manganese and chromium-based austenitic stainless steel having a moderate amount of nickel, copper, and nitrogen.
The grade has a balance of various alloying elements that produce austenitic structure mostly in the annealed condition. This grade type is considered suitable for manufacturing products like J4 stainless steel strip.
However, the lower cost of nitrogen and manganese renders this stainless steel grade economical while endowing this grade with high formability and good strength.
It’s important to be aware that during the latter half of the 20th century, Japan introduced the J4 grade into the stainless steel spectrum. This addition was a component of the “fourth generation” of stainless steel, aiming to rectify issues seen in earlier renditions.
The acronym J4 stands for “Japanese 4th generation,” signifying its Japanese origin. However, due to its remarkable performance, J4 stainless steel has garnered extensive acceptance and usage beyond its country of origin.
J4 stainless steel finds widespread application in diverse products such as industrial machinery, culinary equipment, and automotive components. Various industries prefer it owing to its exceptional mechanical strength and resistance to corrosion.
The chemical composition of J4 stainless steel
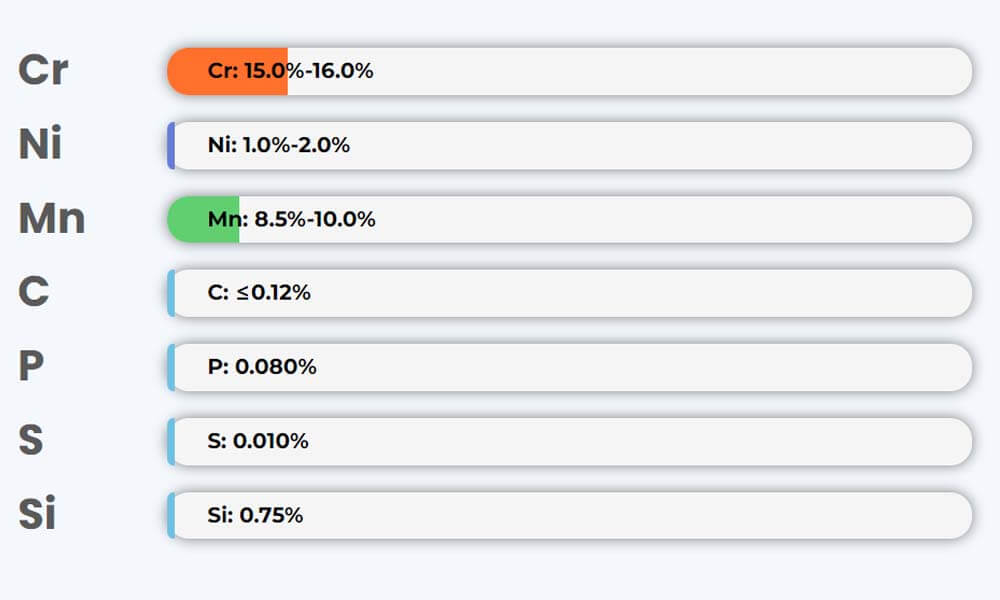
| Element | Carbon | Manganese | Sulfur | Phosphorus | Silicon | Chromium | Nickel |
| Grade J4 | 0.1 | 8.5~10 | 0.010 | 0.080 | 0.75 | 15 – 16 | 1.0~2.0 |
The mechanical properties of J4 stainless steel
Grade | Yield Strength 0.2% offset (KSI) | Tensile Strength (KSI) | % Elongation (2″ Gauge length) | Hardness rockwell B |
J4 | 325 min | 650 min | 40 min | 100 max |
What are the features of J4 stainless steel?
Exceptional Flexibility and Resilience
Distinguishing J4 stainless steel are its remarkable malleability and sturdiness. High ductility allows materials to bend without fracturing under stress, while superior toughness enables greater durability against impact before fissures occur. J4 stainless steel’s combination of high ductility and toughness facilitates easy shaping and welding, maintaining strength and corrosion resistance.
These characteristics render J4 stainless steel particularly suitable for automotive and manufacturing sectors, where shaping and welding are common practices. Applications demanding longevity and enduring performance benefit from its high ductility and resilience, preventing deformation and cracks.
High Strength and Hardness
Opting for J4 stainless steel provides an excellent solution when seeking high strength and hardness in a stainless steel grade. The blend of strength and stress-resistant attributes makes this grade a preferred choice in constructing buildings and manufacturing industrial machinery. Among ferritic stainless steels, J4 exhibits impressive tensile strength, reaching up to 620 MPa.
With the potential to attain a Rockwell hardness of 93, J4 stainless steel is notably resistant to scratching and bending. Its durability and resistance to wear make it a versatile material for various applications.
Aided by its low carbon content, J4 stainless steel boasts exceptional strength and hardness. While carbon typically enhances strength and hardness, it also introduces brittleness. J4’s low carbon content ensures both robustness and ductility, resulting in outstanding mechanical properties.
Magnetic Properties
J4 stainless steel displays exceptional ferritic stainless steel attributes, notably corrosion resistance and magnetism. Its pronounced ferromagnetism facilitates effortless magnetization, retaining its magnetic properties even after the magnetic field ceases.
This magnetic feature expedites identification and sorting throughout production. J4 stainless steel is often identified using magnetic detection methods due to its magnetic characteristics.
Compared to other ferritic stainless steels like 430 and 434, J4 possesses high ferromagnetism, although slightly less magnetic. This divergence stems from distinct chemical compositions—J4 contains less iron and more chromium than the mentioned grades.
Malleability
The superior malleability of J4 stainless steel allows easy shaping into various sizes and forms without fracturing. This quality renders it suitable for intricate components in automobiles and household appliances.
Cost-Efficiency
J4 stainless steel stands out as a cost-effective option among stainless steel choices. This attribute makes it particularly appealing when cost considerations are paramount, as seen in mass-produced consumer goods.
Additional Features
J4 stainless steel’s copper content contributes to a reduced work hardening rate. Additionally, its slight magnetism post-cold working allows for comparison to 304 stainless steel. This grade finds application in various mechanical strengths based on cold-working degrees.
Furthermore, a comparison between J4, 304, and 430 stainless steel grades is possible. Notably, J4 exhibits strength comparable to 304 and 430, being 50% stronger. It also surpasses both grades in wear and abrasion resistance.
Moreover, J4 has lower nickel and chromium content than 304, yet higher nitrogen content. This positions J4 well for mild to medium corrosive environments.
What are the uses of the J4 stainless steel?
J4 stainless steel boasts distinct attributes that make it a versatile material suitable for numerous applications. Some prevalent industrial uses of J4 stainless steel encompass:

- Automotive: In the automotive realm, J4 stainless steel finds extensive employment due to its exceptional strength, endurance, and corrosion resistance. It serves as a preferred choice for crafting components like exhaust systems, mufflers, and parts exposed to elevated temperatures and corrosive environments.
- Manufacturing Field: Within manufacturing, J4 stainless steel is employed to fabricate essential tools such as pressure vessels, tanks, and pipe systems. Its combination of purity and robustness makes it an ideal choice, and it’s also employed for crafting appliances tailored for the food industry due to its durability and hygiene.
- Construction Industry: The construction industry benefits from J4 stainless steel’s robustness, extended lifespan, and corrosion resistance. It plays a pivotal role in constructing diverse structures including monuments, skyscrapers, and suspension bridges.
- Chemical Industry: J4 stainless steel occupies a significant place in the chemical industry where resistance to corrosion is paramount. It is a prominent material for crafting reactors, tanks, and pipelines used in chemical processes.
FAQs of J4 Stainless Steel
Is J4 stainless steel food-safe?
In straightforward terms, indeed, J4 stainless steel is deemed safe for use with food. Its strong resistance to corrosion and high tolerance to heat render the J4 grade suitable for food-related purposes. This grade finds application in various catering and food processing items.
Because of its ability to resist corrosion, robust tensile strength, and hygienic attributes, J4 stainless steel is commonly employed in producing equipment used for food processing. This encompasses utensils, tableware, and cutlery. Beyond these, it’s also applicable in crafting water bottles, fruit displays, and milk containers.
How much does J4 stainless steel cost?
The J4 grade represents the premium tier within the J series category. Among the five variations within this series, the J4 grade stands as the most costly due to its elevated copper content.
Additionally, it finds widespread usage in applications involving drawing products and salt picking. Following the sequence, the J4 grade is succeeded by J1, J3, J2, and J5.
The pricing of J4 stainless steel can be influenced by various factors including market conditions, the specific grade, dimensions, and the volume of material acquired. The distinct attributes and diverse applications of J4 stainless steel can justify a higher price compared to other J-grade stainless steel variants.
What exactly differentiates J4 stainless steel from 304 stainless steel?
Although both J4 stainless steel and 304 stainless steel are grades of stainless steel.
304 grade steel contains a minimum of 8% Nickel and J4 has a minimum of only 1% Nickel. The chromium content is also slightly lower.
Conclusion
J4 stainless steel grade offers a cost-effective solution due to its numerous advantageous characteristics and applications.
Furthermore, it boasts recyclability, contributing to its environmentally conscious profile.
Considering these aspects, J4 becomes a viable choice when seeking an economical stainless steel grade. Its comprehensive chemical composition and impressive mechanical attributes position it as an optimal stainless material.












